Turnout inspection in four minutes
PLASSER & Theurer’s new non-contact turnout measuring system records all necessary parameters during a short pass over main and diverging tracks. It also provides detailed image data which can be used to assess the condition of key components or important system parts.
Every turnout must be measured regularly, but doing this by hand requires a great deal of manpower and time. Plasser says this new form of turnout inspection remedies that by allowing the inspection to be carried out in four minutes.
The system is installed on a track inspection vehicle, such as Plasser & Theurer’s EM100VT, and measurement takes place in short intervals between service trains, removing the need for operational restrictions. When measuring multiple turnouts in large stations, the intervals between trains running at night is sufficient. For example, 61 turnouts were measured on the night of March 8 in St Pölten, Austria.
Plasser & Theurer adds that it is not necessary to conduct inspections according to a specific pattern, as the system recognises the pass and correctly assigns it to the relevant turnout. Synchronisation occurs with the aid of master data and GPS.
Smart maintenance through the use of AI and robotics
ALSTOM’S smart maintenance robot is based on a standard robotic platform enhanced with artificial intelligence (AI) software developed by Alstom to improve visual inspections and maintenance efficiency.
Using embedded sensors, the robot is able to map the environment and navigate autonomously on previously defined routes as it surveys various parts of the train, climbing stairs and even avoiding obstacles. The robot automatically captures video and images of components, which are then analysed with the AI software to locate issues and non-compliant components so that faults can be rectified before they cause in-service breakdowns.

The solution offers a number of benefits, including:
- improved maintenance efficiency and quality
- reduced materials consumption thanks to predictive maintenance
- enhanced working conditions and ergonomics, and
- increased fleet availability and reliability.
The robot is currently in the acceleration phase of its development, with SBS Transit testing the technology at the Sengkang depot in Singapore. Here, the solution was able to reduce train maintenance times and significantly improve the quality of inspections.
Battery-powered CD100 B clip driver
THE Clip Driver CD100 B clipping machine is designed to streamline rail projects while easing physical demands when clipping and de-clipping Pandrol Fastclips.
The CD100 B is comprised of a power pack and two clipping tools, featuring an ergonomic design with a weight-bearing wheel that glides along the rail, significantly reducing strain on the operator. While perfect for smaller applications, its versatility allows quick coupling with other equipment, with the added bonus of lifting sleepers by up to 10mm.

The battery-powered CD100 B emits no exhaust and produces minimal noise, making it ideal for use in tunnels and stations.
Advantages include portability and ease of use by a single operator. It replaces manual tools, eliminating risks and offering compatibility with various Fastclip series for functionality and versatility. Thanks to its compact design, the CD100 B is easily transportable in a car, allowing quick use and reduced costs.
First hardware implementations and tests in FRMCS RMR 101 band
FROM carrying out design to conducting lab and field tests of the very first Future Railway Mobile Communication System (FRMCS) prototypes, Kontron Transportation has been deeply involved in many work packages of the 5G Rail project. Within this framework, research and development engineers were mandated with designing new 5G radio units able to operate in the TDD 1900MHz FRMCS frequency band, also known as Rail Mobile Radio (RMR) n101.

Once integrated in the 5G SA test lab network, the n101 gNodeB was then able to provide radio service to the FRMCS onboard gateways that host specific tailor-made chipsets built by Thales in order to achieve the first FRMCS calls in n101 band, using ETCS and ATO applications.
All this was later completed by field tests in real conditions when 1900MHz radio units were deployed in a French National Railways (SNCF) test area near Paris.
Globally, these innovative prototypes enabled 5G Rail members to perform various tests using the specific n101 band. The upcoming reports should inform future FRMCS testing and development.
A digital maintenance solution for operators
TRADITIONAL methods of fleet maintenance can be time-consuming, inefficient, or difficult to coordinate, causing digital onboard systems to incur configuration errors or become vulnerable to targeted cyber attacks. The result can be costly unplanned downtime across the fleet.
To address this concern, RazorSecure has developed the Digital Maintenance Gateway (DMG), a system designed specifically for rail that combines a secure cloud platform with an EN50155 edge device that is integrated onboard the train.
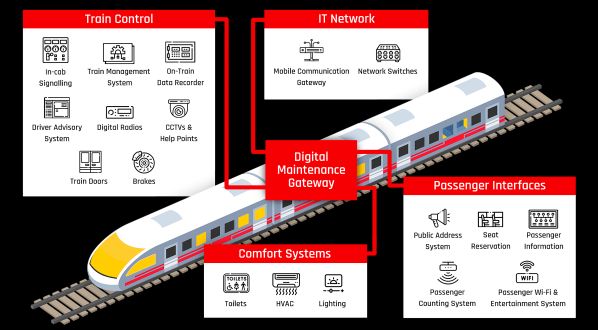
The supplier says the system provides a holistic view of current and planned maintenance needs for maintenance engineers, enabling secure local or remote maintenance access, with each engineer authenticated using unique multi-factor credentials.
It adds that this easy access eliminates the need for dedicated service laptops and USB sticks which can become lost, stolen or damaged. DMG isolates service laptops from potentially insecure onboard systems and prevents the addition of unauthorised applications or malware. It also automates management of software tools and can distribute firmware and configuration files across the fleet instantaneously.
In addition, DMG provides centralised access to manage and apply updates enabling maintenance staff to work more effectively and deploy updates faster.
Electric vehicles for tunnel maintenance
UNDER a contract awarded by Munich City Utilities, Robel has developed track maintenance vehicles with a new drive concept, resulting in noticeable improvement in the environmental and working conditions in tunnels.

The vehicles can travel to the worksite using overhead or third rail electrification, while a battery supplies the power during maintenance operations. An additional diesel generator is available as a backup for long work assignments.
The new multi-function vehicles can carry crew, tools, rails and switches and other materials, and can also carry out traction tasks including the recovery of failed trains. The units are designed for bi-directional operation with a crane at both ends and loading platforms on both sides. Robel says the vehicles can negotiate steep gradients, and can operate in multiples of two or three controlled from one vehicle.
Bringing AI to the railways
WITH a primary focus on safety and reliability, Rail Vision has developed two primary visual scanning products that detect potential hazards, obstacles, and damaged track. Constantly scanning the surroundings of the railway ensures operators take proactive measures while helping drivers to prevent accidents and maintain smoother operations.

Rail Vision says the systems also have the ability to process large amounts of data instantly without cell phone or Wi-Fi connectivity. Their advanced computational unit accurately differentiates between normal conditions and critical events, delivering timely alerts to drivers.
There are several long-term benefits. Collecting and analysing data on performance, infrastructure wear, and potential dangers enables operators to optimise maintenance schedules, streamline operations, and improve overall efficiency and safety.
Part 1 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here
Part 3 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here
Part 4 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here

