Stopping wheel flats in their tracks
PROBLEMS related to wheel flats are extremely expensive and time consuming. Not only do they result in the train being taken out of service, the necessary reprofiling diminishes the life of the wheelsets and increases lifecycle costs.
To help protect wheelsets from flats, several S2R projects involving major rail companies and research institutes and universities in Europe developed and tested a suite of solutions for increasing braking performance in low-adhesion and degraded braking modes.
The DistanceMaster adhesion management solution provides a scalable and comprehensive way to manage low to extremely low adhesion. For example, DM-Adaptive Wheel Slide Protection decreases commissioning risks and the occurrence of wheel flats. The DM-Control+ offers several performance benefits in cases of degraded modes or on gradients, while DM-Smart Sanding helps prevent the intake of sand.
The DM system, which is already in service on more than 200 trains, has proven effective in limiting the number of wheel flats by up to 80%, thus significantly reducing maintenance costs.
One big step towards mainline automation
AUTOMATIC Train Operation (ATO) has the potential to transform rail transport and significant work has taken place within S2R to develop mainline ATO capabilities at Grade of Automation 2 (GoA2).
Spearheaded by the S2R IP2, standard specifications were developed to start the process of migrating ATO towards GoA2. Amongst these specifications are ATO functions such as timetable speed management (TTSM), supervised speed envelope management (SSEM) and automatic train stopping management (ATSM), along with automatic timing point management capabilities such as stopping point (arrival and departure time), passing point (passing time), dwell time computation and door opening and closing.
As a result of this work, infrastructure managers and operators can now deploy automatic driving to reduce operating costs and increase capacity with several projects underway in Europe. RER Line A in Paris is already operating at GoA2 and, as a result, has reduced journey times by 10%. Critically, the initiative has helped to lay the groundwork for a smooth migration to full automation at GoA4.
Breaking down the silos for multimodal travel
TRYING to plan a multimodal journey can be a frustratingly fragmented process for passengers, involving numerous digital platforms and several service providers. However, this could change due to the work of the Shift2Rail-supported Innovation Programme 4 (IP4).
IP4 developed the Travel Companion, an intuitive web-based system, also available as a mobile app, which serves as a one-stop-shop for seamlessly planning and managing a multimodal journey, utilising all available modes of transport, from train to bus, bike and car-sharing and even walking. It offers a suite of services for all stages of a trip, including before, during and after. Crucially, it does not require a change in legacy system for Transport Service Providers (TSP) and is scalable at a European level.
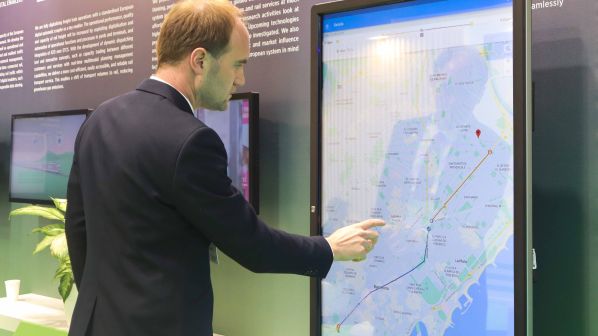
The solution is based on the IP ecosystem, which makes use of the ontology approach to facilitate the integration of any kind of TSP without the need for time-consuming custom integration. In addition, it also allows TSPs to define mobility packages, following the concept of mobility as a service (MaaS). The whole ecosystem provides a lower barrier to entry to multimodal mobility offerings, which is particularly important for smaller TSPs.
Once the trip is planned, customers can use the same solution to book tickets and make reservations, all of which are stored within the application. When it’s time to go, passengers can once again rely on their Travel Companion to monitor for delays or disruption and, if needed, make immediate adjustments to the journey plan.
Optimising operations through prediction
IRREGULARITIES such as debris on the tracks or a mechanical malfunction can have a major impact on rail services.
The key to preventing such system-wide issues is predicting when they will happen - which is exactly the function of Intelligent Asset Management Systems (IAMS) such as that developed by the S2R-supported IN2SMART2 project. The project developed an innovative IAMS equipped with decision-support methodologies and algorithms for anomaly detection.

The platform, which is currently in use on Milan’s metro Line 5, uses track circuit monitoring to identify potential false occupancy of block sections. It also leverages machine learning models to accurately predict anomalies that could disrupt the service and impact passengers. Together, these capabilities allow the infrastructure manager to remotely monitor the diagnostic status of the track circuits and schedule maintenance accordingly.
The IAMS also features anomaly detection models for forecasting degradation of train wheels, statistical analysis of the most frequent alarms and the most degraded assets, decision-support system functions for alternative maintenance scheduling based on asset status, and an integrated human-machine interface customised to specific user needs.
Part 1 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here
Part 2 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here
Part 3 of IRJ Innovations Showcase 2023 can be found here

